Contribution Guide
Welcome to the SCION contribution guide! If you are interested in contributing to the project, this page will help you out on your journey to your first SCION commit.
Hint
If you have any questions, you can always find us on our Slack workspace or on our Github project page. Do not hesitate to ask us anything, or feel free to just drop by and say “Hi”.
Please use this invite link to join scionproto Slack workspace.
What skills do you need to contribute?
SCION is a complex project, and uses a lot of different technologies. If you are unfamiliar with some of them, we have compiled a list containing some great resources to get you started.
Language |
Contribution area |
Tutorials |
|---|---|---|
Go |
SCION Control-plane, SCION Data-plane, SCION Tools |
|
Python, Bash |
Acceptance testing, Helper scripts |
Coming soon |
Starlark |
Bazel build/test system |
Coming soon |
For version control, we use Git and GitHub. For more information about using Git (including links to resources to get you started if you’ve never used before), please visit How to Use Git and GitHub.
No matter what language you want to contribute to, one of the first steps to take is to set up a development environment. See Setting up the Development Environment for the needed steps. If you encounter issues, please visit our Slack and ask for help.
Souce code map
Because the code is mostly written in Go and hosted on a public repository, its inline documentation is rendered automatically at https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/scionproto/scion and includes a helpful index.
Finding an issue to contribute to
We use GitHub labels to categorize issues in the SCION tracker. The two most interesting categories when searching for something to contribute to are:
Help wanted issues. These are issues that nobody is working on at the moment, and are up for grabs.
Good first issue issues. These are usually Help wanted uses that are somewhat simpler. These are a good place to start if you’ve never contributed to the project before.
Once you find something you like, post a comment on the issue announcing that you’re interested in working on it. This initial message signals to others that somebody is already working on it (and thus avoids duplicate work), and also is the first step in gathering more information about the issue from the SCION team.
From this point on, somebody from the SCION maintainers team will reach out to you and guide you for the rest of the process. If you have any questions, please remember to shoot us a question on our Slack.
Finally, make sure that the code you write adheres to the SCION project Style Guides.
Governance: TC Implementation
The Technical Committee (TC) Implementation of the SCION Association are the custodians of the open-source SCION implementation projects.
People
The current members of the TC Implementation are:
Jean-Christophe Hugly ( @jiceatscion, @jiceatscion)
Dominik Roos ( @oncilla, @Dominik Roos)
François Wirz ( @FR4NK-W, @frank)
Lukas Vogel ( @lukedirtwalker, @luke)
Marc Frei ( @marcfrei, @marcfrei)
Jordi Subirà ( @JordiSubira, @Jordi Subirà-Nieto)
Markus Legner ( @mlegner, @Markus Legner)
Responsibilities and Tasks
The TC Implementation has the following main responsibilities, as defined in its charter:
Coordination with the Association Board and other bodies of the SCION Association. In particular, coordinate with the TC Standardisation to synchronise the evolution of the SCION standards, specifications, and their implementation. Consult with the Advisory Board on strategic planning.
Steering strategic direction of the open source SCION project(s); planning projects aligned with priorities of SCION Association members and the open source developer community.
Deciding on cross-cutting issues such as development processes, guidelines, tooling, etc.
The TC may define technical teams and work groups and delegate tasks. No technical teams or work groups are currently defined.
Where not delegated to technical teams, the TC Implementation members participate in the day-to-day operations to implement the Change Proposal Process defined below, in particular by
Participating in change proposal discussions and moderating discussions
Reviewing and deciding over individual change proposals and pull requests
Change Proposal Process
Many changes, including bug fixes and documentation improvements, can be implemented and reviewed via the normal GitHub pull request workflow.
More substantial changes must be submitted as a proposal in the form of a GitHub issue, in order to create a consensus among the SCION community. Typical examples for substantial change proposals include:
Adding, changing, or removing components or functionality
Changing interfaces between components
Proposals for changes to the SCION protocol (e.g., header format, processing rules, cryptography) are currently following the same process. This may, however, change in the near future when a formal specification or standard for the SCION protocol is established.
Hint
It is recommended to discuss proposals with other (senior) developers before submitting them, for example on our Slack.
Warning
Pull requests for substantial features that did not go through the proposal process will be rejected or put on hold.
Formal Process
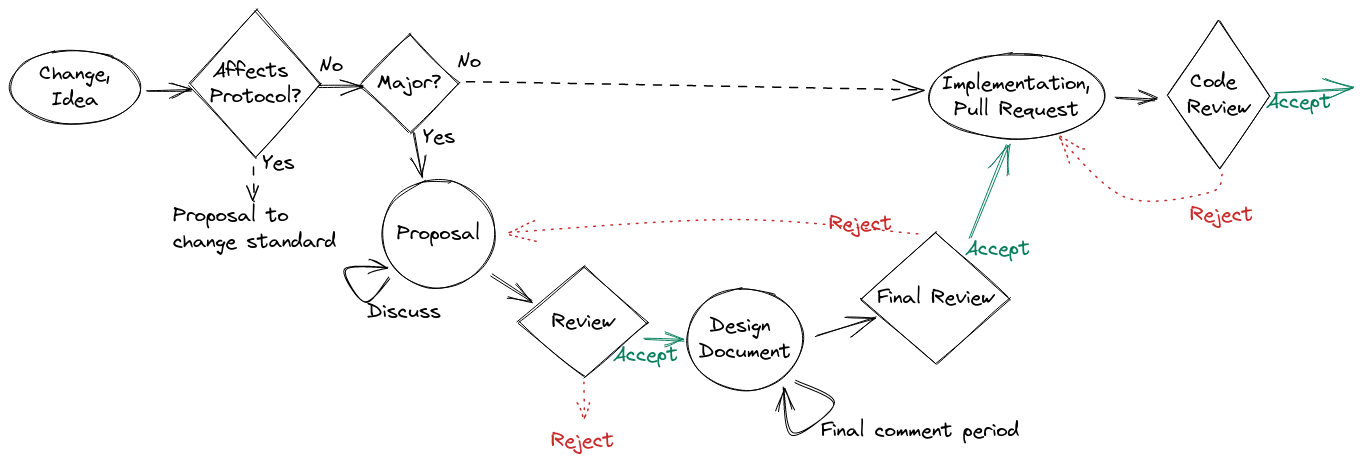
- Creation:
To open a proposal, the author submits a GitHub issue following the
proposaltemplate.- Review:
The proposal may receive feedback from the community, which should be incorporated by the author. Moreover, the assigned technical team triages the proposal and assigns one of its members to manage the process. The technical team discusses the proposal and provides feedback. To increase transparency, the results of these discussions are summarised publicly.
- Decision:
The technical team decides to accept, postpone, or reject the proposal based on the outcomes of the discussion and feedback from the community.
- Initial Design:
If the proposal has been accepted, the authors complete an initial design document and submit it to the repository (doc/dev/design) in the form of a pull request. The design document has the status WIP and is linked to the WIP section of Design Documents. Once that pull request is approved and merged, the proposal issue is closed. A new issue (following the
Work Itemtemplate), owned by the design proponent, is open to track its evolution towards its final form. The title of the issue may be of the form:<topic>: finalize design.- Design Improvements:
Multiple revisions to the WIP document may be submitted and reviewed as PRs. Participants may discuss any change required via the tracking issue.
- Final review:
Once the document reaches a form that appears consensual, the technical team starts the final comment period, together with a proposition to accept, postpone, or reject the design.
The final comment period lasts ten calendar days and is advertised, such that stakeholders have a chance to lodge any final objections before a decision is reached. If no major comments are raised during the final comment period, the proposed action (accept, postpone, reject) is acted; otherwise, the proposal goes back to the review step and is discussed further.
Following the decision, the document’s status is changed to one of Active, Postponed, or Rejected, the design document is linked to the corresponding section of the index, and the tracking issue is closed. If the design’s new status is Active, a new tracking issue is open for its implementation.
- Implementation:
The design is implemented typically, but not necessarily, by the authors. The implementation is submitted as one or more pull requests. The implementation will be reviewed; acceptance of the design does not automatically imply that its implementation will be accepted.
Once the implementation is deemed complete, the design document’s status is changed to Completed, it is linked to the corresponding section of the index, and the implementation tracking issue is closed.
Should a decision be made to abandon or postpone the implementation, the design document’s status is changed to Postponed, Outdated, or Rejected; depending on the reason for the decision.
Learning resources
See also
- Setting up the Development Environment
Get started by cloning the repository and installing the build tools.
- Running SCION Locally
Run a SCION network on your development machine
- Wireshark
Install Wireshark and the SCION packet dissector plugin to inspect packets on the wire.